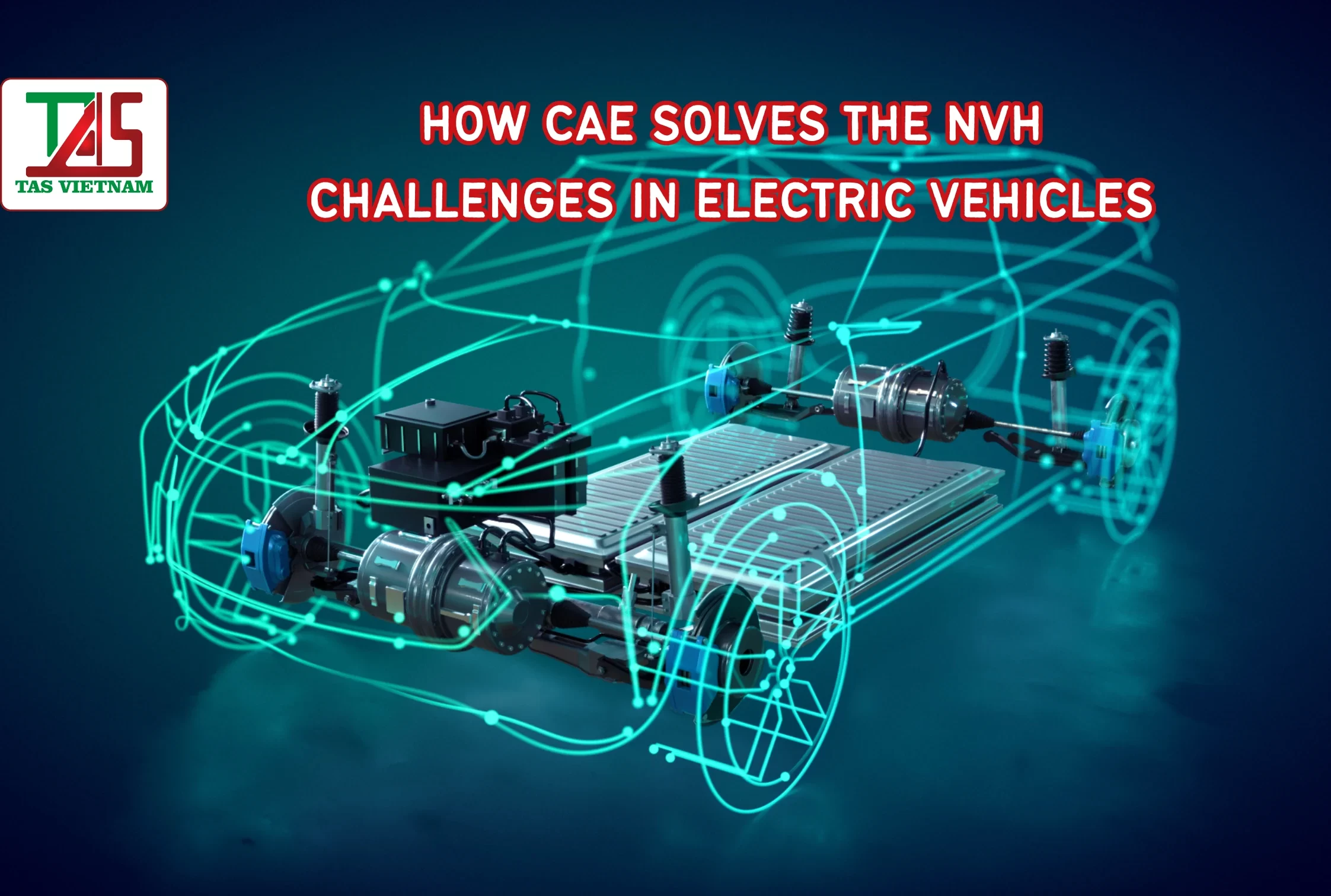
Electric vehicles (EVs) are fundamentally changing the automotive landscape, offering clean mobility, instant torque, and a quieter driving experience. Yet ironically, this “quietness” has introduced new engineering challenges. With the internal combustion engine (ICE) gone, the familiar masking noise disappears—leaving room for previously hidden noises to become more noticeable. Wind hiss, tire noise, high-frequency whines from electric motors, and structural vibrations suddenly dominate the acoustic environment.
For automotive engineers and manufacturers operating in Vietnam, Japan, the U.S., and Europe, solving NVH (Noise, Vibration, Harshness) in EVs is now a top priority. And with development cycles becoming shorter, CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) has emerged as an essential solution for identifying noise sources, predicting acoustic behavior, and optimizing components before building prototypes.
This article explores the new NVH realities of electric vehicles, the role of advanced simulations such as acoustics and vibration analysis, and how TASVINA’s CAE engineering expertise helps companies achieve quieter, more refined electric mobility.
1. The New Sources of Noise in Electric Vehicles
In ICE vehicles, engine combustion noise typically contributes the most dominant acoustic signature. When this is removed in EVs, engineers face a new set of noise contributors:
1.1 Wind Noise
At higher speeds, aerodynamic noise becomes much more noticeable because there is no engine noise to mask it. Key sources include:
-
Mirror-induced turbulence
-
A-pillar separation
-
Door/Glass sealing imperfections
-
Airflow leakage around the cowl area
Wind noise is difficult to debug late in development, making early simulation crucial.
1.2 Tire and Road Noise
Tire-road interaction becomes one of the loudest contributors in EVs:
-
Contact patch friction
-
Sidewall vibration
-
Structural transmission through suspension arms and subframes
Engineers must understand both airborne and structure-borne paths to effectively treat them.
1.3 High-Frequency Electric Motor Whine
Unlike ICE engines, electric motors generate:
-
High-frequency tonal harmonics
-
Inverter switching noise
-
Electromagnetic vibration of stator and rotor components
These tones fall into the 400 Hz – 8 kHz region—very sensitive to the human ear.
1.4 Component and Accessory Vibration
Other systems become more audible in EVs:
-
HVAC compressor
-
Battery cooling pump
-
Inverters and converters
-
Interior plastic components
Even minimal vibrations can be perceived as rattles or buzzing.
2. Why CAE is Essential for EV NVH Development
Traditional hardware testing cannot keep up with the complexity and speed required for modern EV programs. CAE enables engineers to simulate, predict, and optimize NVH behavior upfront.
2.1 Acoustic Simulation (Acoustics CAE)
Acoustic CAE helps engineers:
-
Model sound propagation inside and outside the vehicle
-
Identify loud zones, resonance cavities, and weak insulation points
-
Evaluate design changes without physical prototypes
Simulations commonly used:
-
Boundary Element Method (BEM)
-
Finite Element Method (FEM)
-
Acoustic Transfer Vector (ATV) analysis
-
Cabin sound pressure prediction
This ensures targeted, data-driven material placement—saving cost and weight.
2.2 Vibration and Structural Analysis
Structure-borne noise is a major challenge in EVs. CAE allows engineers to:
-
Identify vibration modes of motor housings, battery packs, and brackets
-
Predict resonance with road excitations
-
Evaluate stiffness and damping performance
-
Optimize mounts and bushings in the suspension
Techniques include:
-
Modal analysis
-
Frequency Response Function (FRF)
-
Random vibration analysis
-
Harmonic response
2.3 Multi-Physics Analysis (EM + NVH)
Electric motors require coupled simulations:
-
Electromagnetic forces → cause vibration
-
Vibration → causes high-frequency acoustic whine
CAE integrates electromagnetic and structural simulations to predict tonal noise early.
2.4 Faster Development, Lower Cost
By addressing NVH during digital design:
-
Fewer prototype iterations
-
Lower testing cost
-
Faster validation
-
More confidence before production
This is essential for OEMs and suppliers competing in global markets.
3. Practical Example: How TASVINA Uses CAE to Reduce High-Frequency Motor Noise
At TASVINA, our engineering team frequently supports international clients in Vietnam with EV NVH challenges. One common issue is a high-frequency tonal peak coming from the electric motor, typically caused by electromagnetic excitation.
3.1 Step 1 — Identify Harmonic Noise Sources
Using electromagnetic simulation, engineers calculate:
-
Magnetic forces acting on stator
-
Harmonic order distribution
-
Switching frequency contributions from inverter
This identifies which frequencies may cause audible whining.
3.2 Step 2 — Structural Vibration Simulation
Next, TASVINA performs:
-
Modal analysis of motor housing
-
Frequency response analysis
-
Coupled electromagnetic-mechanical vibration simulation
The goal is to find structural resonances that amplify noise.
3.3 Step 3 — Acoustic Prediction
Using BEM or FEM acoustic simulation, we predict:
-
Radiated sound power
-
Cabin noise impact
-
Contribution of mounts and connectors
Hotspots become visible early in the digital phase.
3.4 Step 4 — Optimization
We evaluate improvements such as:
-
Changing motor housing rib thickness
-
Adjusting electromagnetic coil pattern
-
Adding damping materials
-
Modifying inverter switching strategy
-
Strengthening the mounting bracket
A small structural modification often reduces the tonal peak by 3–7 dB.
4. Engineering Solutions for EV NVH: What Works Best?
4.1 Acoustic Insulation Optimization
CAE determines:
-
Best material thickness
-
Placement of absorption/insulation layers
-
Lightweight engineering constraints
This ensures maximum noise reduction with minimum mass.
4.2 Suspension and Subframe Optimization
By predicting structure-borne pathways, engineers can:
-
Reinforce load paths
-
Tune bushing stiffness
-
Improve modal separation
-
Reduce road rumble
4.3 Battery Pack and Cooling Systems
CAE identifies vibration hotspots in:
-
Cooling pumps
-
Liquid hoses
-
Battery enclosures
Minimizing these prevents annoying rattles.
4.4 Aerodynamic Noise Refinement
Using CFD + aeroacoustics simulation:
-
Reduce A-pillar vortex
-
Optimize mirror geometry
-
Improve sealing systems
5. How TASVINA Supports Global Automotive Clients in Vietnam
TASVINA provides full-cycle CAE and engineering simulation services for international companies operating in Vietnam. Our capabilities include:
CAE Services
-
Structural NVH simulation
-
Electric motor acoustic analysis
-
Vibration analysis for suspension & chassis
-
Multi-physics coupling (EM + NVH)
-
Acoustic BEM/FEM simulation
-
Durability & fatigue analysis
-
Thermal and CFD simulation
Why Clients Choose TASVINA
-
Experienced engineering team
-
High-quality technical reporting
-
Support for Japan, U.S., Vietnam, and EU markets
-
Flexible and cost-effective outsourcing
-
Strong understanding of global automotive standards
Whether you are an OEM, Tier-1 supplier, or engineering firm, TASVINA helps accelerate your EV development with reliable CAE solutions.
Conclusion
As electric vehicles become increasingly refined, NVH performance is emerging as a critical competitive differentiator. The silence of EVs reveals new acoustic challenges—from high-frequency motor whine to structural vibration and wind noise. CAE offers a powerful way to identify problems early, reduce development costs, and deliver a superior user experience.
With deep expertise in acoustics, vibration, and multi-physics simulation, TASVINA is ready to support global automotive companies seeking high-quality NVH engineering solutions in Vietnam.