Description
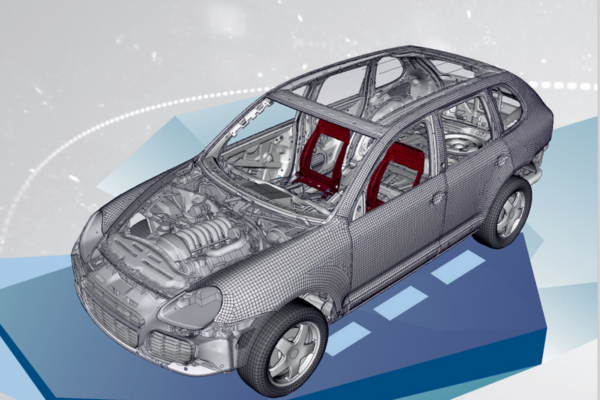
Meshing is the process of dividing a continuous model into discrete elements (such as triangles, tetrahedrons, hexahedrons) to simulate the behavior of materials and structures under various influences. Meshing plays an extremely important role in CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) because it directly affects the accuracy and performance of the simulation.
Meshing Techniques from 1D, 2D, 3D:
There are various meshing techniques chosen based on the size and complexity of the model:
1.1 Meshing from 1D Model:
- Used for bar-like models (such as beams, springs).
- Uniform Division: The model is divided into elements of equal size.
- Graded Division: The model is divided into elements that gradually increase or decrease in size according to a specific ratio.
1.2 Meshing from 2D Model:
- Used for plate-like models (such as metal sheets, vehicle shells).
- Triangular Mesh: The model is divided into triangles.
- Quadrilateral Mesh: The model is divided into quadrilaterals.
- Mixed Mesh: A combination of triangles and quadrilaterals.
1.3 Meshing from 3D Model:
- Used for any 3D models.
- Tetrahedral Mesh: The model is divided into tetrahedrons.
- Hexahedral Mesh: The model is divided into hexahedrons (cubes, rectangular boxes).
- Mixed Mesh: A combination of various element types.
Evaluating Mesh Quality:
The quality of the mesh directly impacts the accuracy and performance of the simulation. Therefore, mesh quality must be evaluated before performing the simulation. Some common evaluation criteria are:
- Element Size Ratio: The ratio between the maximum and minimum element sizes must be reasonable to ensure accuracy.
- Element Shape Quality: Mesh elements should have good shapes, avoiding distorted or overly narrow elements.
- Mesh Transition: Mesh elements should transition smoothly between different areas of the model.
- Convergence Capability: The simulation solution should converge as the number of mesh elements increases.
Importance of Meshing in CAE Analysis:
- Affecting Accuracy: A coarse mesh can lead to significant errors, while an overly fine mesh can require extensive computational time.
- Affecting Performance: The more detailed the mesh, the longer the computation time. It is crucial to balance accuracy and performance when creating the mesh.
- Affecting Convergence: The mesh must be created such that the simulation solution converges, meaning the results do not change significantly when the number of mesh elements is increased.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.