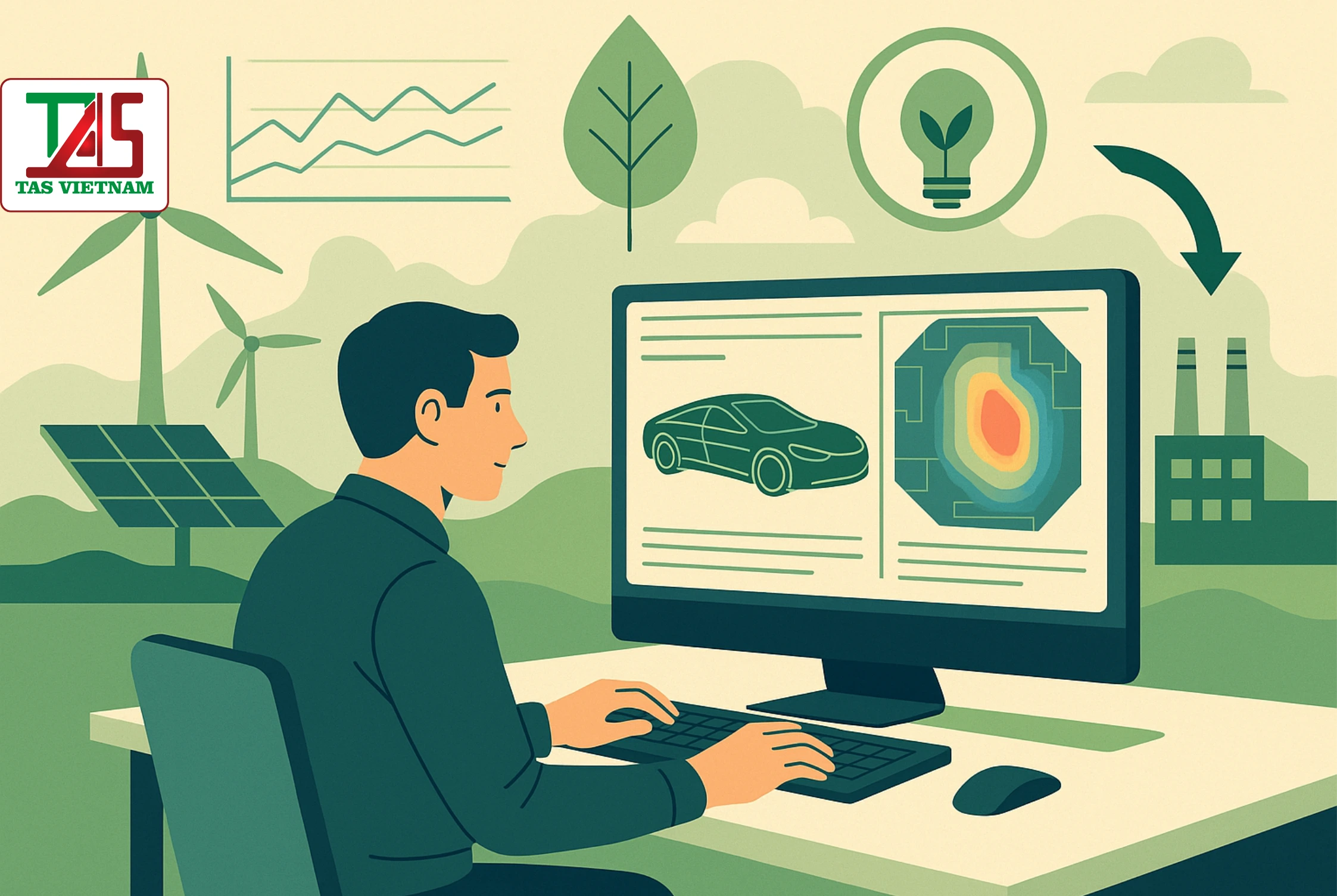
1. Global Context: Towards Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Products
As industries worldwide strive to meet stricter carbon reduction and sustainability standards, such as ISO 14001 and the EU Green Deal, companies are rethinking the way they design and manufacture products.
Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) has emerged as a strategic enabler in this transformation — allowing engineers to design, test, and optimize products that are greener, lighter, and more energy-efficient even before physical prototypes are made.
2. CAE – The Core Technology for Green Design
CAE integrates simulation tools such as Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), and Multibody Dynamics to evaluate product performance, durability, and energy efficiency.
By leveraging CAE, companies can:
- Reduce physical testing, saving materials and costs.
- Optimize structure and material usage, minimizing waste.
- Predict product behavior and lifetime under real-world conditions.
Through these capabilities, CAE significantly reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions across the entire product lifecycle — from development to operation and recycling.
3. Enhancing Energy Efficiency Through Simulation
CAE is especially powerful in thermal and fluid flow simulation, which enables engineers to understand how products behave under various energy and environmental conditions.
Examples include:
- Automotive: Improving vehicle aerodynamics can reduce drag and fuel consumption by up to 10–15%.
- Electronics: Simulating heat transfer to design efficient cooling systems without additional fans or power.
- Renewable Energy: Optimizing turbine blades or solar panel modules to maximize energy conversion efficiency.
CAE empowers engineers to evaluate hundreds of design alternatives virtually, choosing the one that delivers the best performance-to-energy ratio.
4. Lightweight Design – The Key to Sustainable Products
Lightweight engineering is at the heart of energy-efficient design.
Using CAE, engineers can:
- Reduce component weight by 30–40% without compromising strength.
- Select alternative materials such as composites or aluminum alloys.
- Apply topology optimization to eliminate unnecessary mass.
The result is a lighter, more energy-efficient product that also reduces carbon footprint during manufacturing and operation.
5. CAE in R&D – From Simulation to Innovation
CAE is not just a simulation tool — it is an innovation accelerator.
By integrating CAE early in the R&D process, companies can:
- Shorten product development cycles by up to 50%.
- Increase prototype success rates through precise virtual validation.
- Adopt digital twin workflows that combine design, testing, and data analytics.
With the integration of AI and High-Performance Computing (HPC), CAE is evolving into a system capable of automated design optimization, achieving higher efficiency and sustainability at lower costs.
6. Industrial Applications of CAE
Automotive & Mobility:
- Aerodynamics, structural integrity, thermal management.
- Design of hybrid and electric vehicle systems for energy efficiency.
Electronics & Consumer Devices:
- Thermal design, vibration, and mechanical durability analysis.
- Optimization for lightweight and compact designs.
Manufacturing & Energy:
- Simulation of turbines, compressors, and mechanical systems.
- Fatigue and vibration analysis for extended lifespan.
Construction & Infrastructure:
- Structural analysis to minimize material use.
- Passive energy-efficient building design.
7. TASVINA – Driving Sustainable Design in Vietnam
As a CAE and product design service provider, TASVINA supports both local and international clients in Vietnam through:
- Comprehensive FEA, CFD, and Motion analysis services.
- Engineering consultation and digital design solutions for product optimization.
- Professional training to strengthen in-house R&D capabilities.
TASVINA is committed to promoting a sustainable engineering ecosystem, enabling enterprises to design smarter, greener, and more energy-efficient products.
8. Conclusion
CAE empowers engineers to develop greener, more efficient products and helps companies lead the transition toward sustainable manufacturing.
With technologies like CAE, AI, and simulation-driven design, pioneers such as TASVINA are shaping the future of energy-efficient, environmentally responsible product development.