The automotive industry is undergoing a rapid digital transformation. As vehicles become more complex—with advanced electronics, lightweight materials, and intelligent control systems—traditional design and testing methods are no longer sufficient. Manufacturers now seek faster development cycles, reduced physical prototypes, and improved reliability under real-world operating conditions.One technology leading this transformation is the Automotive Digital Twin, a virtual replica of a vehicle that continuously evolves using CAE simulations, real-time IoT sensor data, and machine-learning-based analytics. This convergence enables a powerful new capability: predictive failure analysis. For engineering teams and international companies operating in Vietnam, Digital Twin technology offers a practical pathway...
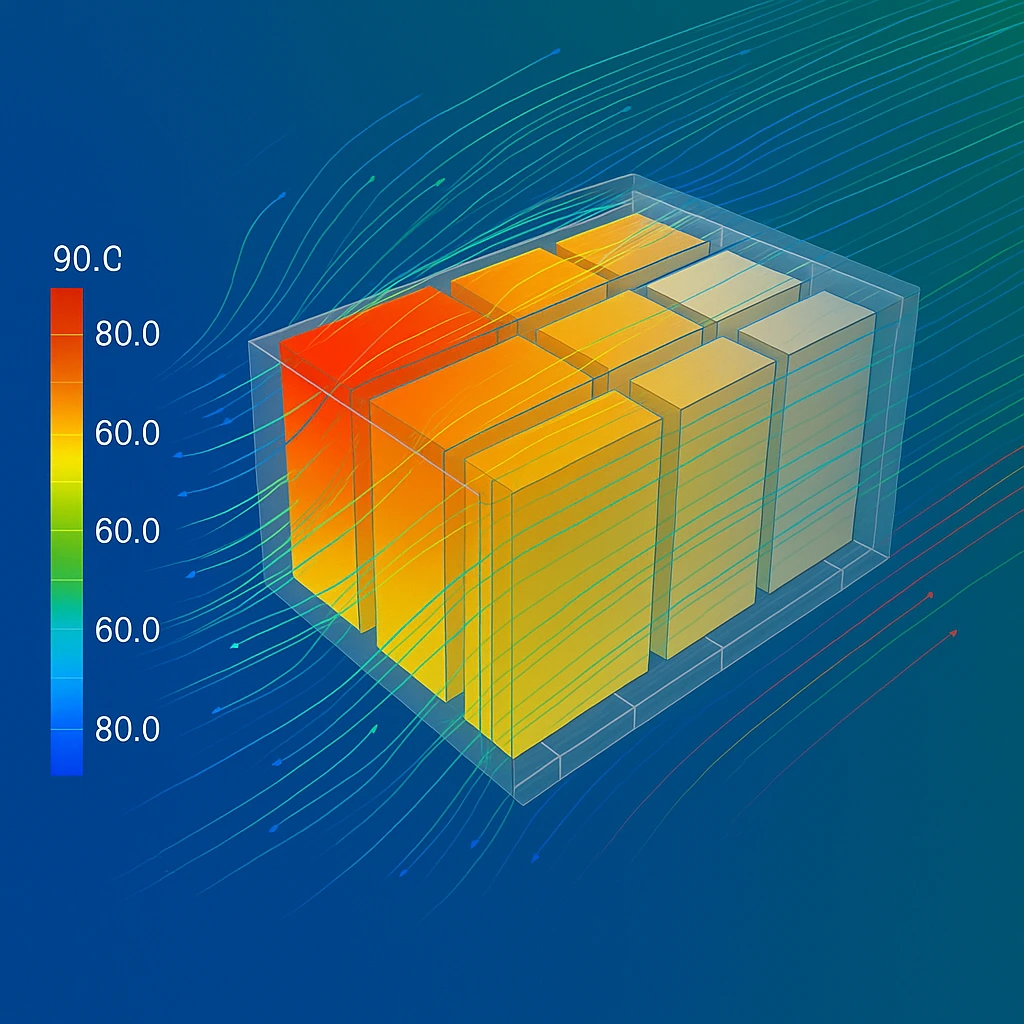
Introduction As electrification accelerates across automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment, battery performance has become a critical engineering concern. Among the many challenges in battery development, thermal behavior remains one of the most decisive factors affecting safety, lifespan, and efficiency. Excessive heat can lead to capacity loss, rapid degradation, thermal runaway, and even catastrophic failure. For global engineering teams operating in Vietnam, the need for accurate, scalable, and real-time battery thermal insights has never been greater. At TASVINA, our Thermal CAE and CFD simulation services enable manufacturers and R&D groups to predict, evaluate, and optimize heat generation and dissipation in...